Introduction to Worker Agents
Worker Agents are autonomous AI agents that process structured, repeatable work through a queue-based system. They continuously monitor for new Work Items and process them automatically based on the runbook you have defined. Work Items are units of work that contain payloads, status information, and execution history. Worker Agents pick and execute them without manual intervention.
While Conversational Agents are optimized for interactive dialogue, Worker Agents operate as "always-on" background processors. They excel at automating end-to-end workflows, reacting to enterprise events, and providing real-time operational visibility through Work Items and dashboards.
Why build Worker Agents?
- Automate end to end work: Take action immediately when new documents or tasks arrive without any manual triage.
- Real time status & auditability: Track every Work Item through its complete lifecycle (Pending → Executing → Completed/Failed/Needs Review ) with detailed logs.
- Scale with demand: Workers continuously poll for new tasks and can easily scale to handle workload fluctuations.
- React to enterprise events: Trigger work based on emails, apps, AWS Lambda, S3, and more using flexible JSON payloads.
Choose Worker Agents when you need queue-driven processing with clear operational control and audit trails. They are ideal for document intake, reconciliations, validations, and back-office workflows.
Key concepts related to Worker Agents
- Work Item: A single unit of work with a JSON payload, optional files/attachments, metadata (tags, priority), and status history.
- Worker Agent: Intelligent AI agent that autonomously processes Work Items based on a defined runbook.
- Trigger: Any event that creates Work Items (e.g., scheduler, email, S3/Lambda, webhooks).
- Runbook: A sequence of steps that define how a Worker Agent processes a Work Item. Written in plain English, the runbook is written similarly to Conversational Agents.
- Control Room: Centralized management platform for deploying, monitoring, and managing agents at scale. The usage of Control Room is exactly the same for Worker Agents as it is for Conversational Agents.
- Work Room: A dedicated interface for managing and monitoring Work Items and Worker Agents. The Work Room provides real-time visibility into the status of Work Items, allowing users to track progress, view history, and pick up items for manual intervention if needed.
Lifecycle of a Worker Agent
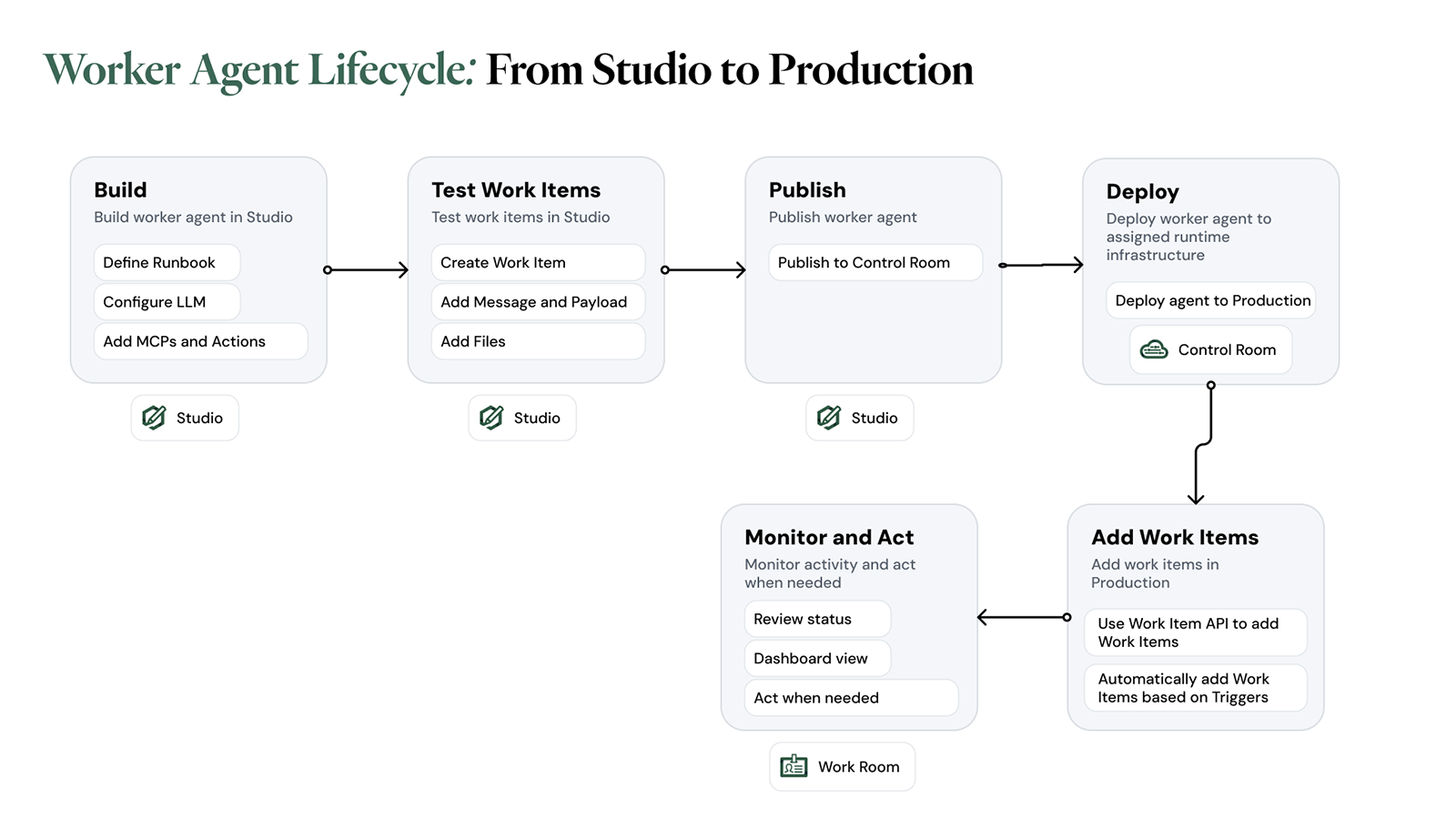
Common use cases for Worker Agents
- Document processing: Automate the intake, extraction, validation, and routing of documents such as invoices, purchase orders, and contracts.
- Data reconciliation: Compare and reconcile data across systems, identify discrepancies, and generate reports.
- Event driven workflows: Trigger workflows based on events such as new email arrivals, file uploads, or database changes.
- Back office automation: Streamline repetitive tasks such as data entry, report generation, and compliance checks.
- Customer support: Automate ticket triage, response generation, and escalation based on predefined criteria.