Explore Worker Agent Runbook & Actions
Worker agents achieve autonomous document processing through the powerful combination of runbooks and actions. Runbooks define document processing workflows in natural language that business users can understand and modify, while actions implement the precise calculations, validations, and system interactions needed to execute those workflows reliably. This separation enables business experts to control how documents are processed while ensuring all calculations, data transformations, and system integrations execute with absolute precision.
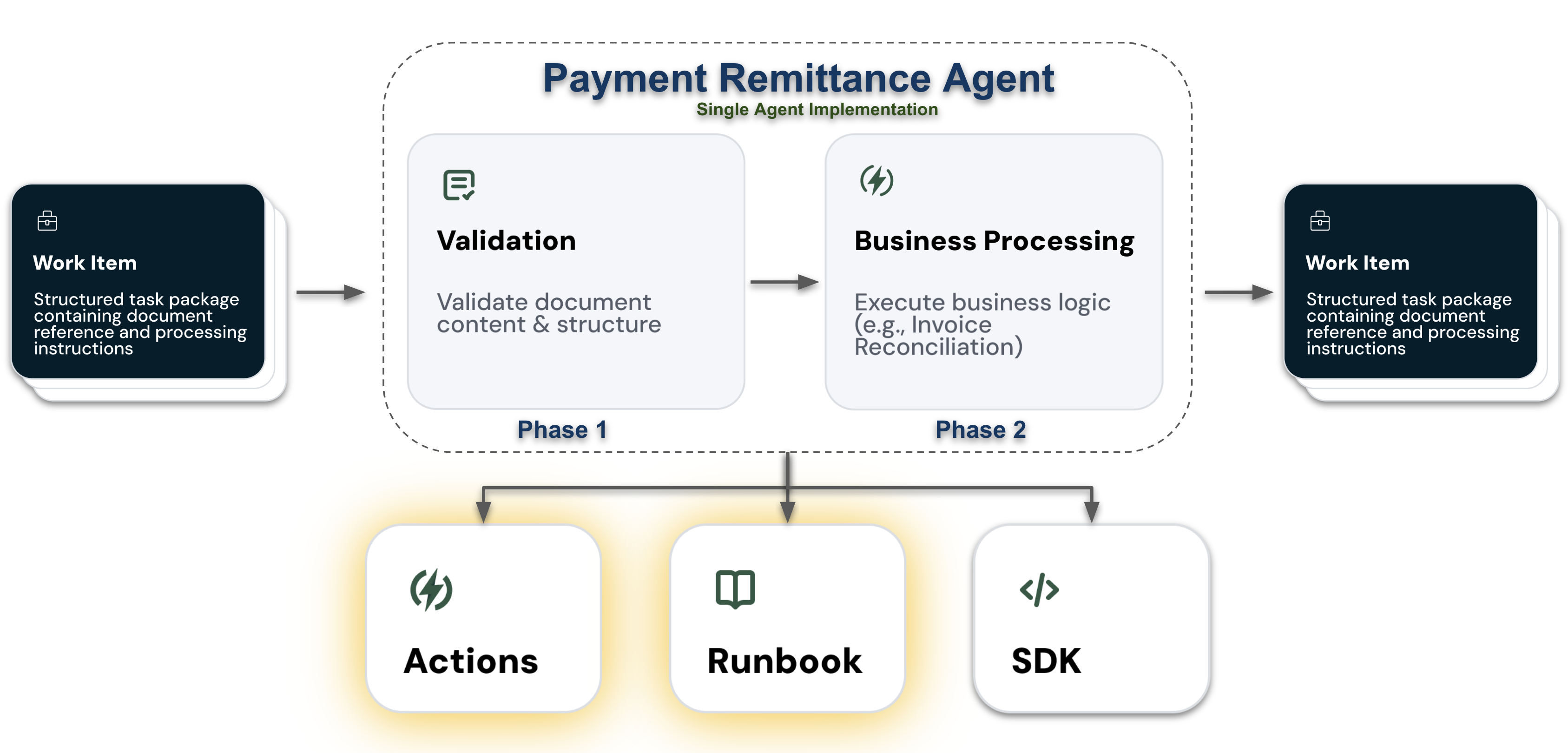
Effective worker agents depend on clear separation between runbooks and actions. Runbooks define business logic in natural language, while actions handle technical implementation with precision. This separation enables business users to control processing flows while ensuring reliable execution.
Understanding Runbooks
A runbook defines how a worker agent processes documents using natural language instructions. It expresses business logic, validation rules, and process flows in a way that business users can understand and modify. Unlike traditional workflow tools that focus on technical implementation, runbooks prioritize business intent and process clarity.

Core Worker Agent Runbook Patterns
Worker agents implement specific patterns that enable autonomous document processing while maintaining business control. These patterns ensure reliable processing across different document types and business scenarios.
Phase Organization
Document processing often requires multiple stages that build upon each other. Runbooks should clearly define these phases, their dependencies, and transition requirements. This ensures systematic processing and maintains data integrity throughout the workflow.
Process Requirements
Worker agents need clear rules about how processing should flow, including sequential requirements, validation steps, and state transitions. Runbooks should define these requirements in business terms while leaving technical implementation to actions.
Business Rules and Outcomes
Worker agents apply business rules to determine processing outcomes. Runbooks should clearly define these rules and their implications, enabling business users to modify criteria without touching technical implementation.
Error Handling Strategies
Worker agents must handle various error scenarios. Runbooks should define how to respond to different types of errors, when to engage users, and what information to provide for resolution.
Working with Actions
Actions are specialized Python functions that implement the technical operations required by worker agents. They handle precise calculations, data transformations, and system integrations that require deterministic behavior and error handling.
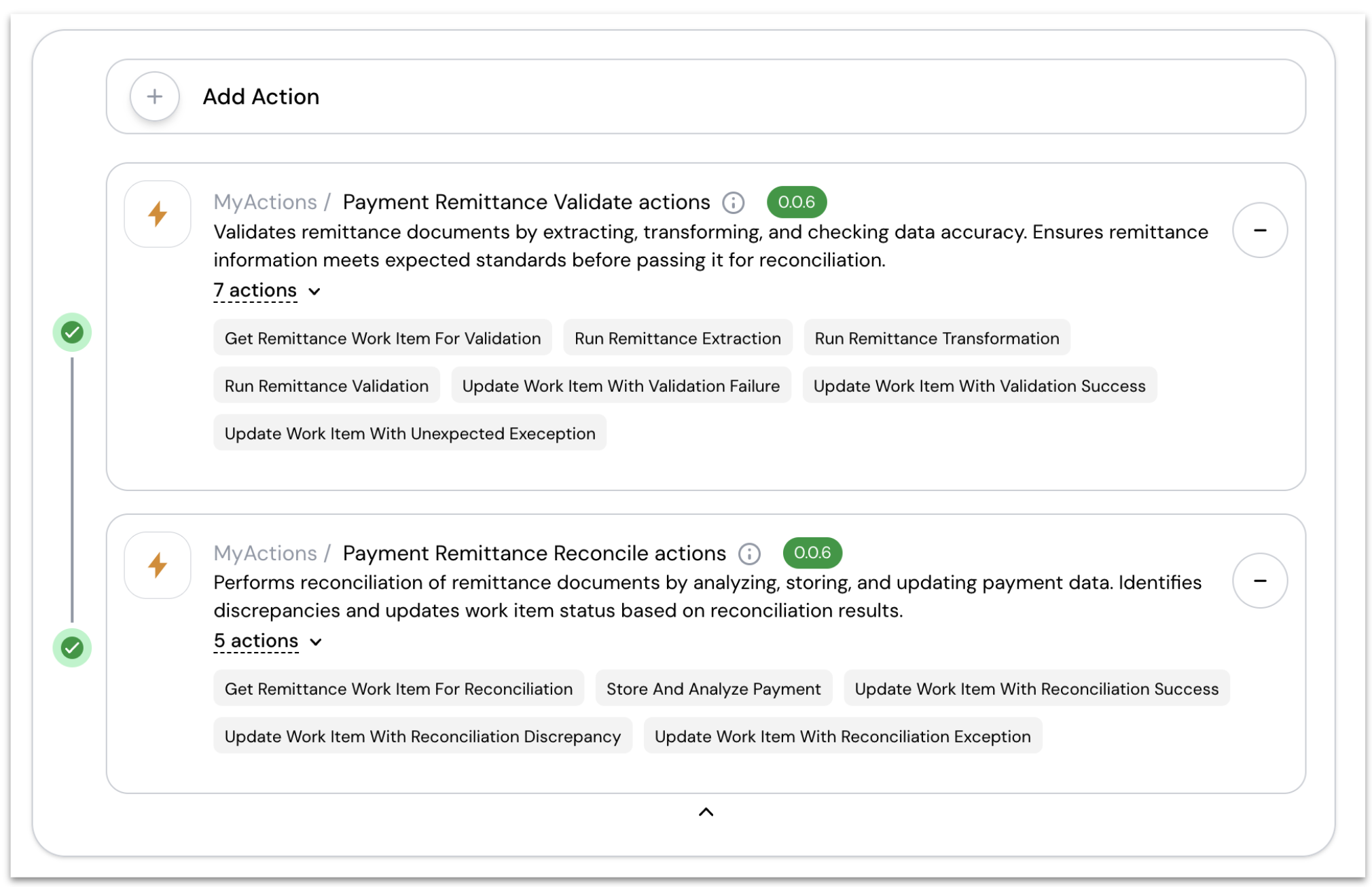
Actions handle precise operations while the runbook orchestrates their use. This separation allows business users to modify process flows while maintaining technical precision where needed.
Understanding Worker Agent Actions
Worker agents typically organize actions into logical packages based on their role in document processing. The Payment Remittance Agent, for example, uses two distinct action packages:
- Validation Actions - ensure document integrity through extraction, transformation, and validation
- Reconciliation Actions - handle payment matching and financial calculations
Core Document Intelligence Actions
All worker agents rely on Document Intelligence APIs wrapped up in actions for managing document data and state:
@action
def get_remittance_work_item(remittance_id: str) -> DocumentWorkItem:
"""
Retrieve work item details including document content and processing state.
Always called at the start of each processing phase.
"""
doc_intel_client = create_di_client()
return doc_intel_client.get_document_work_item(remittance_id)
@action
def store_computed_content(document_id: str, content: dict) -> None:
"""
Store processing results in document database.
Called after significant state changes or computation.
"""
doc_intel_client = create_di_client()
doc_intel_client.store_computed_content(content)Validation Actions
The validation phase requires a sequence of actions that progressively ensure document integrity:
# Document extraction and structure validation
@action
def run_remittance_extraction(remittance_id: str):
"""
Extracts and validates document structure:
- Processes raw document content
- Validates document completeness
- Ensures required sections present
"""
# Data transformation and standardization
@action
def run_remittance_transformation(remittance_id: str):
"""
Standardizes data formats and computes fields:
- Normalizes field formats
- Computes derived values
- Prepares data for validation
"""
# Business rule validation
@action
def run_remittance_validation(remittance_id: str):
"""
Applies business validation rules:
- Validates field relationships
- Checks computation accuracy
- Ensures business rule compliance
"""
# Status management
@action
def update_work_item_with_validation_success(
remittance_id: str,
validation_success_summary: str
):
"""Updates work item status after successful validation"""Processing Actions
The processing phase (reconciliation in our example) uses actions that implement core business logic:
# Payment analysis and storage
@action
def store_and_analyze_payment(remittance_id: str):
"""
Performs comprehensive payment analysis:
- Stores payment details securely
- Executes multi-level reconciliation:
- Total payment matching
- Facility-level validation
- Invoice-level reconciliation
- Generates detailed analysis results
"""
# Status management for different outcomes
@action
def update_work_item_with_reconciliation_success():
"""
Handles successful reconciliation:
- Updates work item status
- Stores reconciliation results
- Generates success report
"""
@action
def update_work_item_with_reconciliation_discrepancy():
"""
Manages discrepancy workflows:
- Documents discrepancies found
- Prepares discrepancy analysis
- Updates work item for user review
"""Action Design Principles
- Deterministic Behavior: Actions ensure consistent, reliable execution of operations
- Error Handling: Each action implements comprehensive error handling and logging
- State Management: Actions maintain document state through the Document Intelligence Service
- Technical Precision: Actions handle all calculations and data transformations
- System Integration: Actions manage interactions with external systems and services
The runbook orchestrates these actions based on business logic, but the actions themselves handle all technical implementation details, ensuring reliable and precise execution.
Separation of Concerns
The distinction between runbooks and actions is fundamental to worker agent design. Here's why this separation matters and how to maintain it effectively:
Natural Language vs Technical Implementation
Runbooks use natural language to express business intent, making them accessible to business users. They define what should happen and why, but not how. For example, a runbook might specify "Validate that facility subtotals match line item sums" but leaves the actual calculation to actions.
Actions, by contrast, handle all technical implementation details. They manage precise calculations, data transformations, and system interactions. This includes decimal arithmetic for financial calculations, data validation logic, and integration with external systems.
Business Logic vs Technical Operations
Runbooks own business rules and process flows. They define validation criteria, processing requirements, and when to engage users. For example, a runbook specifies that payments over $1,000 require review but doesn't implement the comparison logic.
Actions implement the technical operations needed to execute business logic. They handle threshold comparisons, data aggregation, and state management. This includes input validation, error handling, and maintaining processing state.
Flexibility vs Determinism
Runbooks provide flexibility in business process definition. They can be updated to reflect changing business requirements without modifying technical implementation. This might include changing validation rules or adding new processing steps.
Actions ensure deterministic behavior in technical operations. They implement precise calculations and data handling with proper error checking and logging. This includes maintaining transactional integrity and handling edge cases.
Implementation Guidelines
-
Express Business Logic in Runbooks
- Use clear, business-oriented language
- Define process flows and requirements
- Specify validation and business rules
- Document error handling strategies
- Outline collaboration workflows
-
Implement Technical Operations in Actions
- Handle all calculations and data operations
- Manage system integrations
- Implement error handling and logging
- Ensure proper state management
- Maintain data integrity
-
Maintain Clear Boundaries
- Keep business logic in runbooks
- Implement technical details in actions
- Avoid mixing concerns
- Document interfaces clearly
- Test implementations independently