Table of Contents:
- What is a worker agent?
- The role of worker agents in modern AI architecture
- Worker agents vs other types of AI agents
- How Sema4.ai builds and runs worker agents
- Common use cases for worker agents
- Governance and observability for worker agents
- The future of worker agents in enterprise AI
- Transform your enterprise with worker agents
Worker Agent in AI: What It Is and How It Works
In today’s rapidly evolving enterprise landscape, organizations are increasingly turning to AI automation to streamline operations and enhance productivity. At the forefront of this transformation are worker agents – autonomous AI entities that execute complex tasks and processes on behalf of users and systems. But what is a worker agent exactly, and how do they differ from other AI solutions?
A worker agent represents a sophisticated form of artificial intelligence designed to handle specific operational workloads with minimal human intervention. Unlike simple chatbots or basic automation tools, worker agents leverage advanced AI capabilities to operate in dynamic environments, make intelligent decisions, and adapt to changing conditions while maintaining enterprise-grade security and governance.
This comprehensive guide will explore what worker agents are, how they function within modern AI architecture, and how platforms like the Sema4.ai Enterprise AI Agent Platform are making these powerful tools accessible to enterprises worldwide. Whether you’re an IT leader evaluating AI automation solutions or a business professional seeking to understand the future of work, this article will provide you with the insights needed to navigate the worker agent landscape.
What is a worker agent?
A worker agent is an autonomous software entity that executes tasks, processes, and workflows on behalf of users or systems within an enterprise environment. Unlike traditional automation tools that follow rigid, pre-programmed rules, worker agents leverage artificial intelligence to understand context, make decisions, and adapt their behavior based on changing conditions and requirements.
What are worker agents capable of? These intelligent systems can handle a wide range of operational tasks, from processing documents and managing workflows to integrating with enterprise applications and orchestrating complex multi-step processes. Worker agents operate continuously, often working 24/7 to ensure business processes run smoothly without constant human oversight.
The key distinguishing feature of a worker agent is its ability to combine task execution with intelligent reasoning. While a traditional automation script might break when encountering an unexpected scenario, a worker agent can analyze the situation, determine the appropriate response, and either handle the exception autonomously or escalate it to human operators with relevant context.
In enterprise environments, worker agents serve as digital employees that can be trained using natural language instructions, integrated with existing systems through secure APIs, and monitored through comprehensive governance frameworks. This makes them particularly valuable for organizations looking to scale their operations without proportionally increasing their workforce.
The role of worker agents in modern AI architecture
Worker agents play a crucial role in modern AI automation systems by serving as the execution layer that bridges intelligent decision-making with real-world business processes. In a typical AI architecture, worker agents receive instructions from higher-level planning systems, access necessary data and applications, and execute tasks while providing feedback and status updates throughout the process.
Unlike reactive agents that simply respond to immediate stimuli, worker agents go beyond and operate with a degree of autonomy that allows them to plan sequences of actions, handle exceptions, and coordinate with other agents or human team members. This capability makes them essential components in multi-agent systems where different specialized agents collaborate to accomplish complex business objectives.
The integration of worker agents into enterprise AI architecture enables organizations to create sophisticated automation workflows that can adapt to changing business conditions. For example, a worker agent handling invoice processing might need to coordinate with agents responsible for vendor verification, approval workflows, and payment processing – all while maintaining compliance with financial regulations and company policies.
Modern worker agents also leverage machine learning capabilities to improve their performance over time. By analyzing patterns in their task execution, identifying common exceptions, and learning from human feedback, these agents become more efficient and accurate as they gain experience with specific business processes.
Worker agents vs other types of AI agents
Understanding how worker agents differ from other types of AI agents is essential for organizations evaluating their automation strategy. Autonomous agents represent a broader category that includes worker agents, but worker agents are specifically designed for automated task execution and operational workloads.
Reactive agents are a kind of first generation, less mature worker agent that just respond to environmental changes but lack the planning capabilities that make worker agents effective for complex business processes. Planning agents excel at creating strategies and sequences of actions but may not have the execution capabilities needed to carry out those plans in real-world enterprise environments.
Knowledge-based agents focus on reasoning with information and providing insights, while worker agents are built to take action based on that knowledge. Conversational agents, like chatbots, are designed for interaction and communication with humans, whereas worker agents are optimized for behind-the-scenes task execution.
AI agents in general encompass all these categories, but worker agents occupy a unique position as execution-focused entities that combine intelligent reasoning with practical task completion. They’re typically task-specific, meaning they’re designed and trained for particular business functions, and they’re built to scale operational workloads efficiently and tackle more complex tasks within the enterprise.
The key advantage of worker agents over other AI agent types is their ability to operate independently while maintaining integration with enterprise systems and governance frameworks. This makes them ideal for organizations that need reliable, scalable automation without sacrificing control or compliance.
How Sema4.ai builds and runs worker agents
Sema4.ai provides a comprehensive platform for building, running and managing enterprise-grade AI agents, including specialized worker agents designed for real operational impact. Our approach to agent orchestration and execution sets us apart by making sophisticated AI automation accessible to business users while maintaining enterprise security and governance standards.
The Sema4.ai platform enables organizations to build and deploy worker agents using natural language runbooks rather than complex programming. Business users can define how their worker agents should operate by describing processes in plain English, eliminating the traditional barrier between domain expertise and technical implementation.
Our agent orchestration capabilities ensure that worker agents can coordinate with other systems and agents seamlessly. Through our secure integration framework, worker agents can access enterprise applications, databases, and external services while maintaining complete audit trails and compliance with security policies.
The Sema4.ai platform provides comprehensive lifecycle management for worker agents, from initial development and testing through deployment and ongoing monitoring. Our governed execution environment ensures that worker agents operate within defined parameters while providing real-time observability into their performance and decision-making processes. Learn more about how to work with and supervise your worker agents.
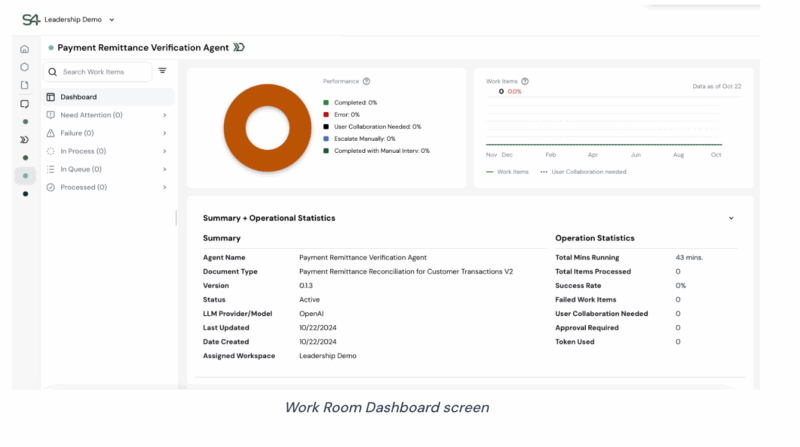
Key features of our worker agent implementation include transparent reasoning capabilities that show exactly how agents make decisions, robust error handling and escalation procedures, and seamless integration with existing enterprise workflows and approval processes.
Transparent reasoning in action
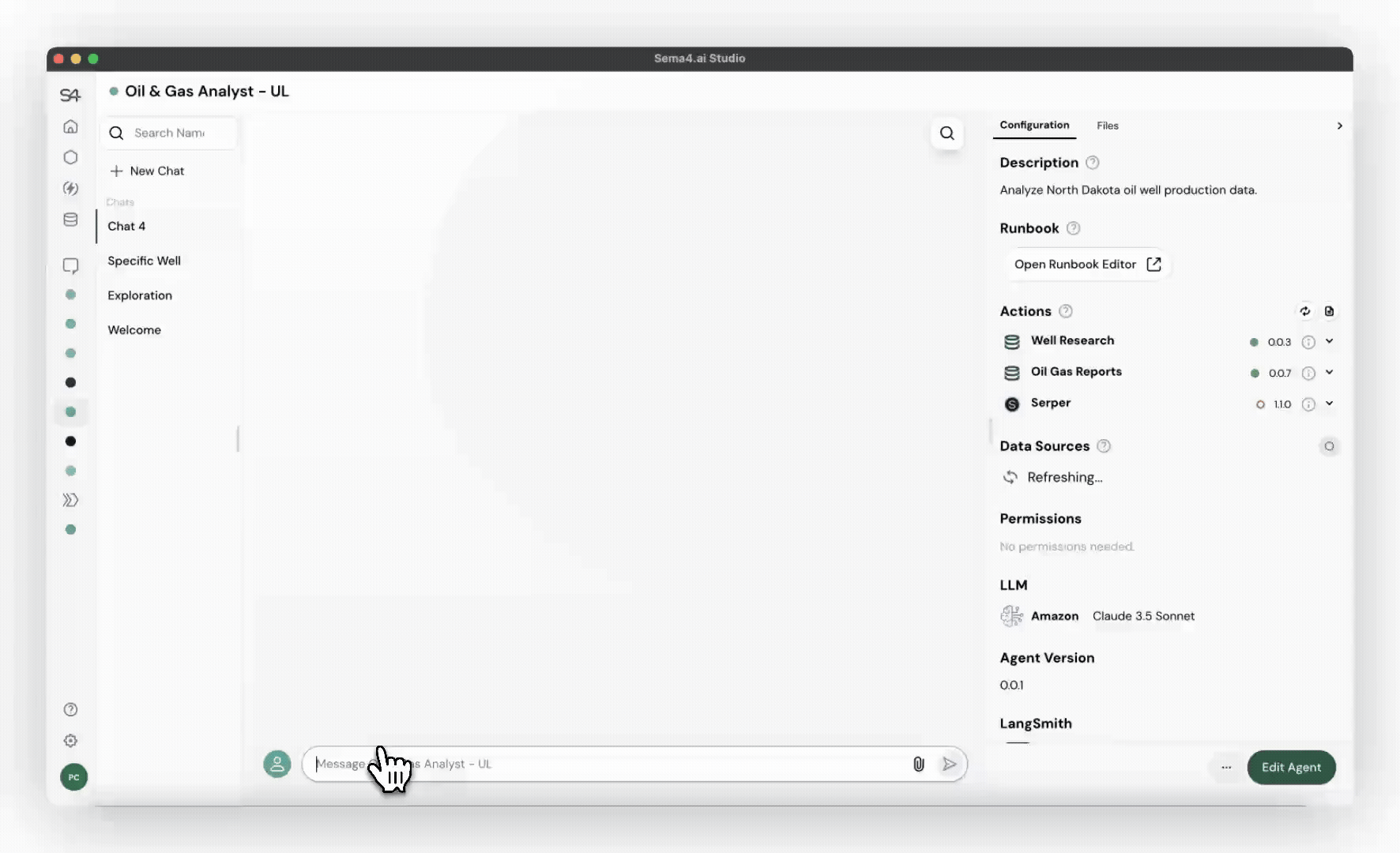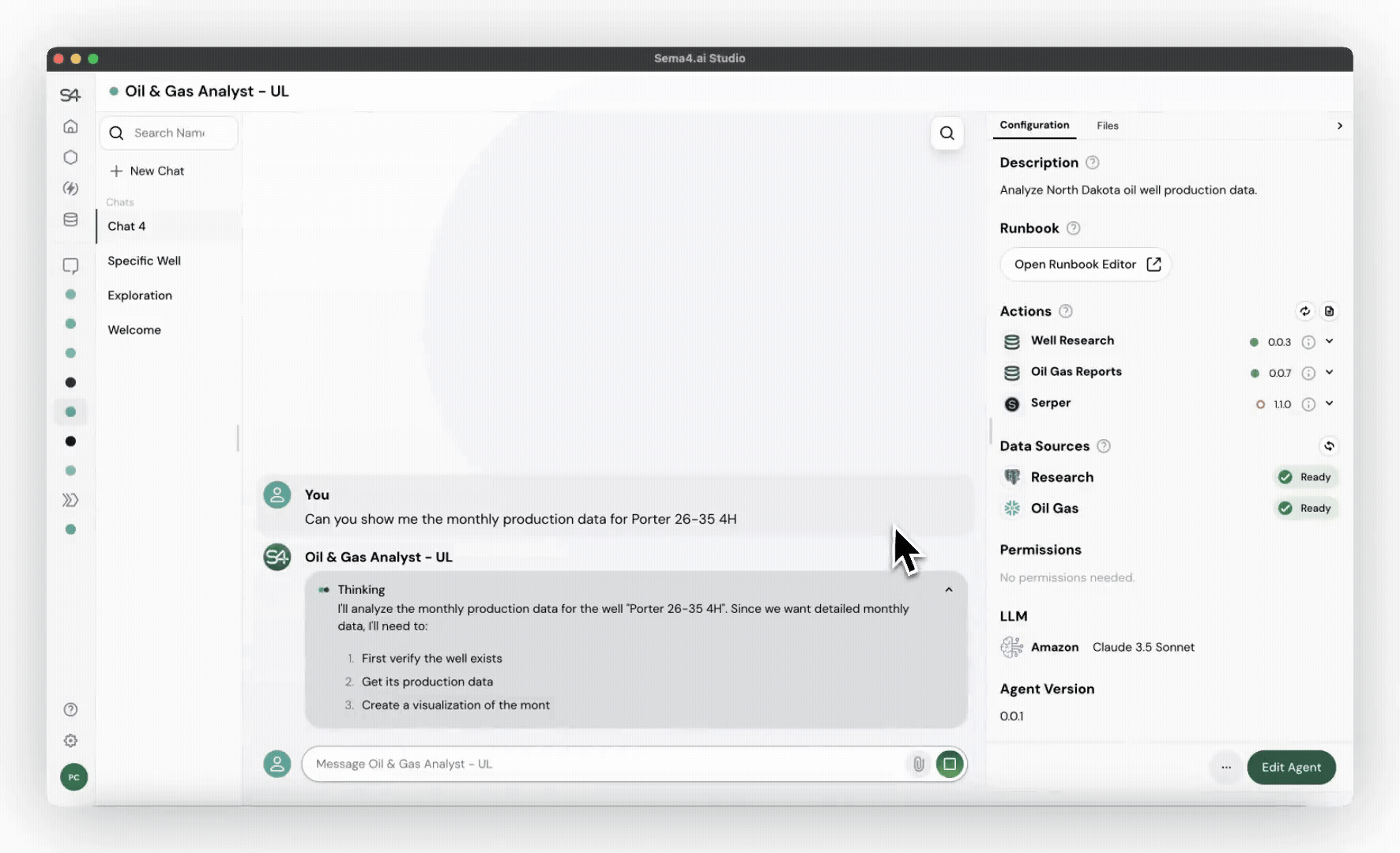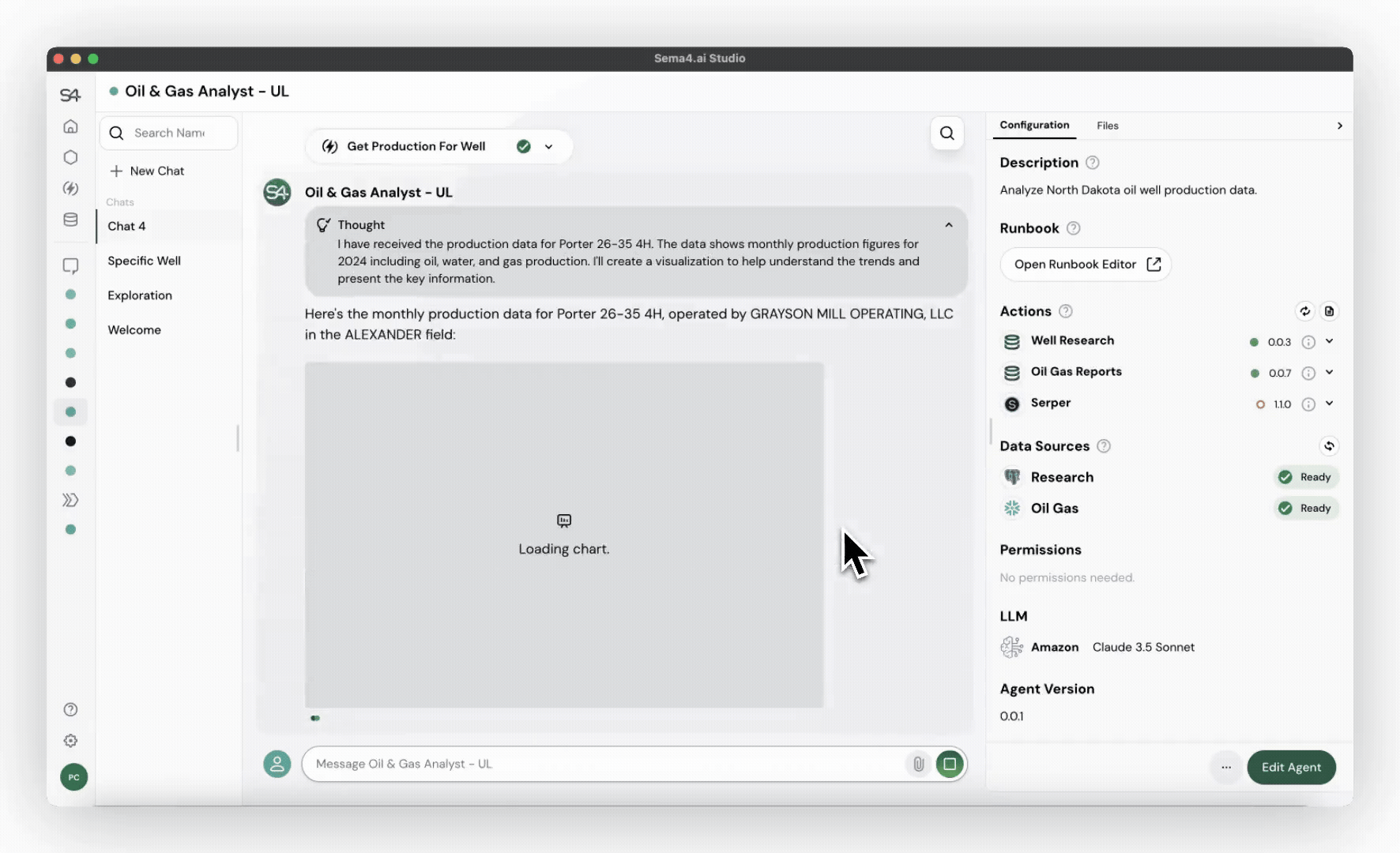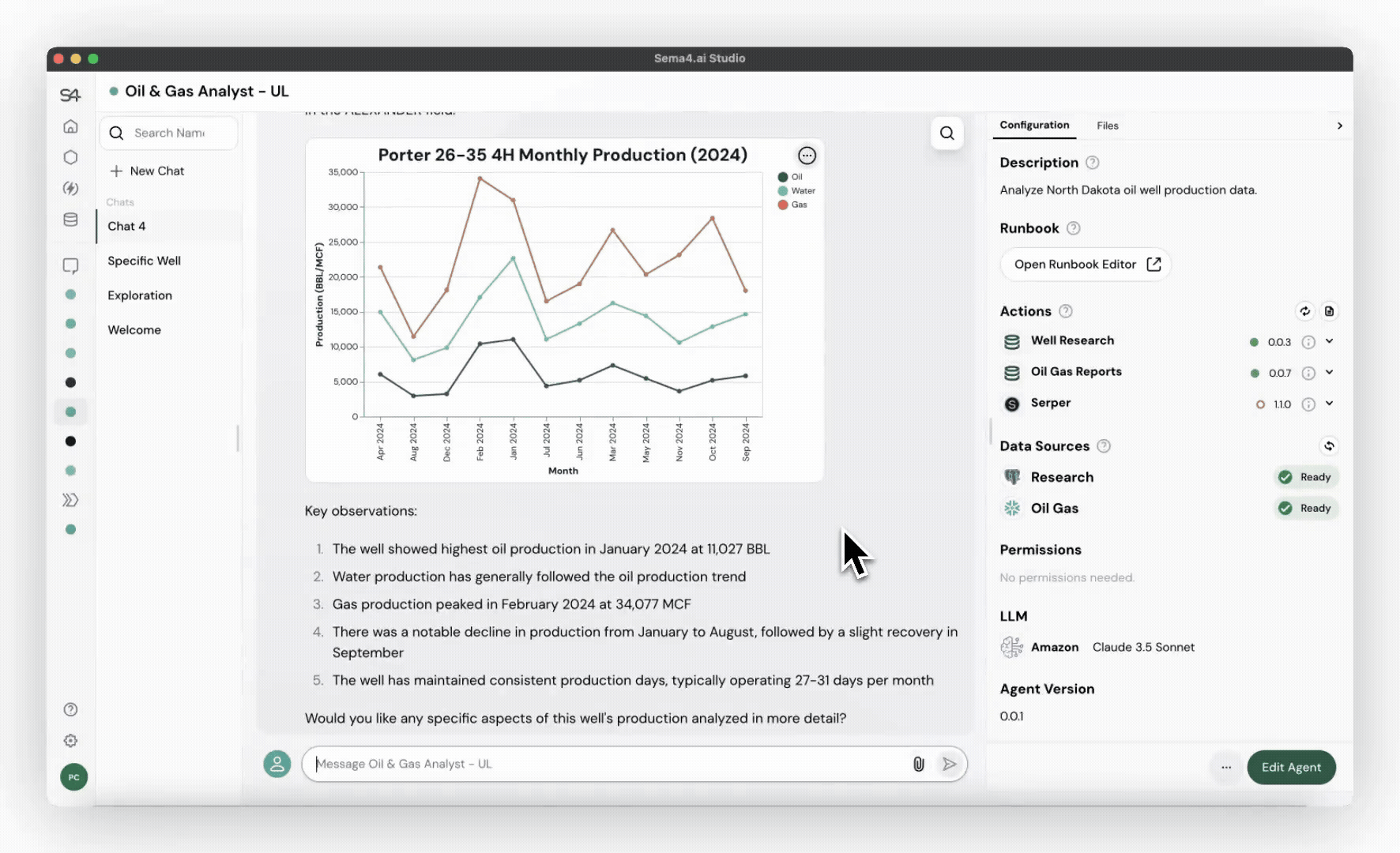
Common use cases for worker agents
Worker agents excel in scenarios where organizations need reliable, scalable automation for repetitive but complex tasks. In IT operations, worker agents handle help desk automation by processing support tickets, diagnosing common issues, and either resolving problems automatically or routing them to appropriate specialists with relevant context and preliminary analysis.
Financial operations represent another strong use case for AI automation through worker agents. These agents can manage invoice processing workflows, handle approval routing based on company policies, perform reconciliation tasks, and ensure compliance with financial regulations. The ability to work continuously means that financial processes can operate around the clock, reducing processing delays and improving cash flow management.
Human resources departments leverage worker agents for employee onboarding workflows, where agents can coordinate multiple systems and stakeholders to ensure new hires receive proper access, training materials, and documentation. Worker agents can also handle routine HR inquiries, benefits administration, and compliance tracking.
Customer operations teams use worker agents to automate CRM task execution, including lead qualification, follow-up scheduling, and data enrichment. These agents can analyze customer interactions, update records across multiple systems, and trigger appropriate next steps in sales or support processes.
The modular and adaptable nature of worker agents means they can be customized for industry-specific requirements while maintaining integration with standard enterprise systems and workflows.
Governance and observability for worker agents
Effective governance and observability are critical for enterprise deployment of worker agents. Sema4.ai’s platform provides comprehensive controls that ensure worker agents operate within defined boundaries while maintaining transparency and accountability.
Role-based access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can create, modify, or deploy worker agents. This governance framework extends to the agents themselves, with each worker agent operating under specific permissions that limit their access to data and systems based on business requirements and security policies.
Comprehensive logging and audit trails capture every action taken by worker agents, creating a complete record of their decision-making processes and task execution. This agent orchestration capability is essential for regulatory compliance and enables organizations to understand exactly how their automated processes are functioning.
Audit logs in Sema4.ai Control Room
Real-time monitoring provides visibility into worker agent performance, including task completion rates, error frequencies, and processing times. This observability enables organizations to optimize their automation workflows and identify opportunities for improvement.
The platform’s governance framework also includes exception handling procedures that ensure worker agents escalate appropriately when they encounter situations outside their defined parameters. This maintains the balance between automation efficiency and human oversight that enterprises require.
The future of worker agents in enterprise AI
The evolution of worker agents represents a fundamental shift toward more autonomous and intelligent enterprise operations. As AI capabilities continue to advance, worker agents will become increasingly sophisticated in their ability to handle complex, multi-step processes that currently require human intervention.
Future developments in worker agent technology will likely include enhanced learning capabilities that allow agents to adapt more quickly to changing business conditions and requirements. Integration with advanced AI models will enable worker agents to handle more nuanced decision-making and exception handling.
The trend toward agent ecosystems, where multiple specialized worker agents collaborate to accomplish complex business objectives, will transform how organizations approach process automation. Rather than building monolithic automation solutions, enterprises will deploy networks of coordinated worker agents that can adapt and scale based on business needs.
Platforms like Sema4.ai are positioning organizations to take advantage of these developments by providing the infrastructure and governance frameworks needed to deploy worker agents safely and effectively at enterprise scale.
Transform your enterprise with worker agents
Worker agents represent a transformative approach to enterprise automation, combining the intelligence of AI with the reliability and governance that businesses require. These task-driven AI entities go beyond simple automation to provide autonomous, adaptable solutions that can handle complex business processes while maintaining transparency and control.
Sema4.ai’s platform makes worker agents practical and scalable for enterprise deployment by providing natural language development tools, comprehensive governance frameworks, and seamless integration capabilities. Organizations can leverage worker agents to automate routine tasks, improve process efficiency, and scale their operations without sacrificing quality or compliance.
As the technology continues to evolve, worker agents will become increasingly central to how enterprises operate, enabling new levels of efficiency and capability while freeing human workers to focus on higher-value strategic activities.
Ready to explore how worker agents can transform your organization?
Read about top enterprise use cases for AI agents.
Learn more about Sema4.ai Agents and discover how our platform can help you build, deploy, and manage intelligent automation solutions.
Learn about how to manage and govern AI agents with Control Room.
Explore our AI Agent Learning Center for additional resources and insights into the future of enterprise AI.


